Laser Systems
AL-IN

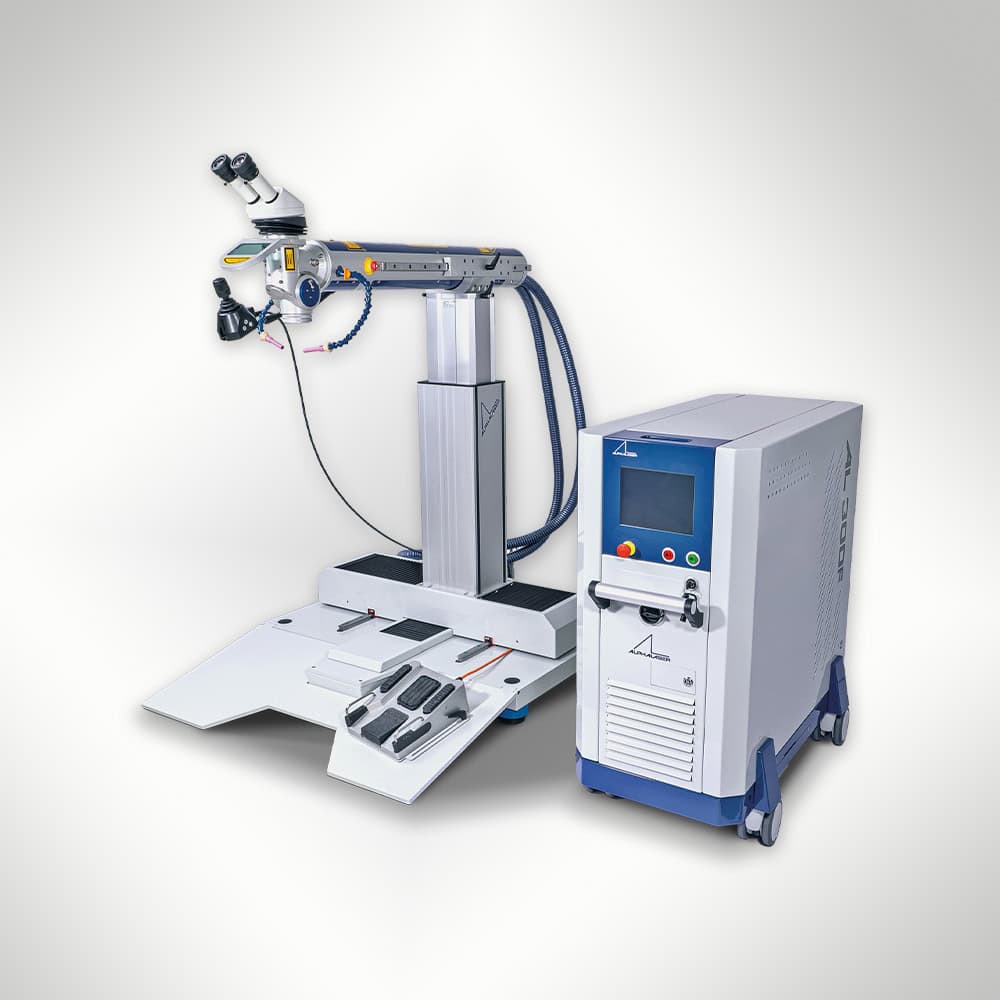
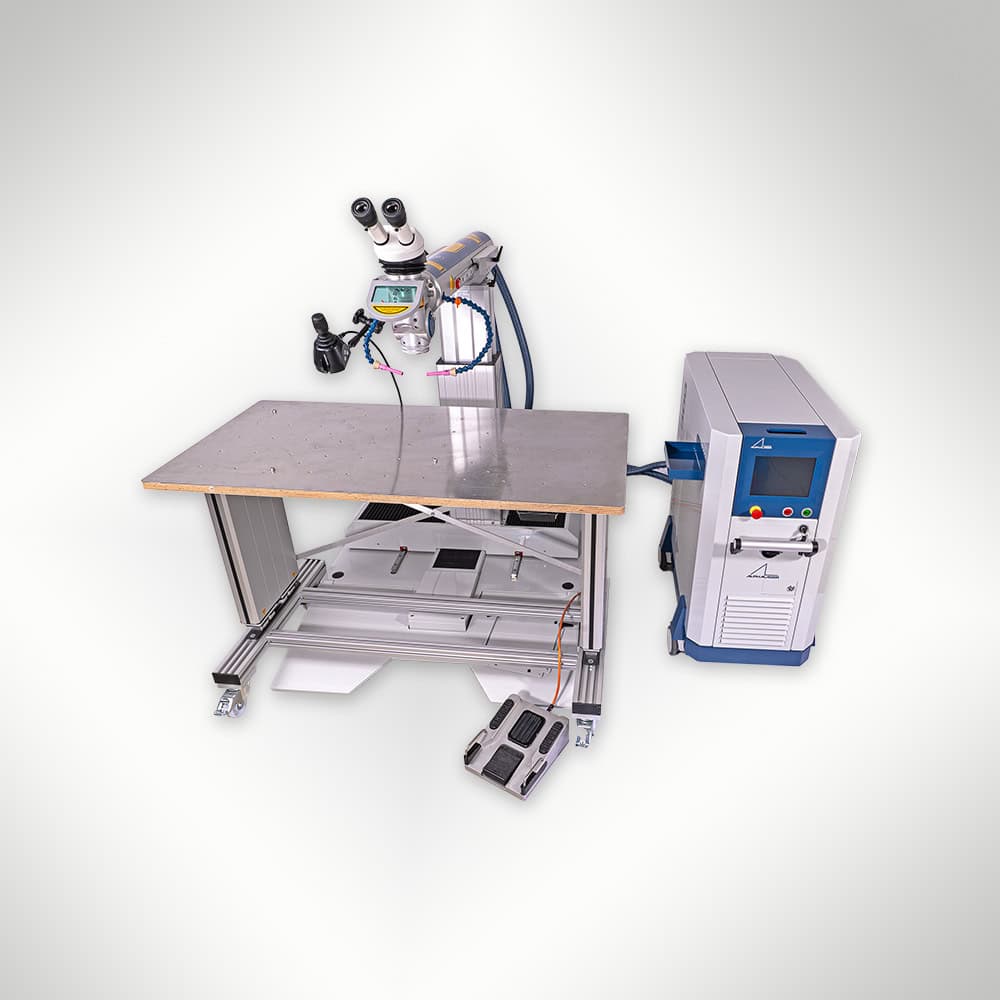
The AL-IN from Alpha Laser is a flexible, stationary laser welding system available in both Nd:YAG and fibre laser models with power options up to 600W. Designed for precision welding, it offers modular configuration for small and large components, making it ideal for tool repair and production tasks.
Models
The AL-IN 120 is equipped with a 120W Nd:YAG laser, delivering 9 kW peak pulse power and 90J pulse energy. It is ideal for fine-detail pulsed welding on small components.
The AL-IN 150 provides 150W Nd:YAG laser power with a peak pulse power of 9 kW. It is suited for moderate precision welding tasks with enhanced energy control.
The AL-IN 200 delivers 200W of Nd:YAG power, designed for medium-scale pulsed welding tasks requiring precise control and reliability in tool repair and manufacturing.
The AL-IN 300 offers 300W of Nd:YAG laser power with a peak pulse power of 9 kW, making it ideal for more demanding welding tasks on larger components.
The AL-IN 150F fibre laser provides 150W of power with a peak pulse power of 1.5 kW and 15J pulse energy. It supports both pulsed and CW welding, ideal for delicate tasks on heat-sensitive materials.
The AL-IN 300F offers 300W of fibre laser power with a peak pulse power of 3 kW and pulse energy of 30J. It supports pulsed and CW modes for flexible, precision welding on metals and alloys.
The AL-IN 450F provides 450W of fibre laser power with a peak pulse power of 4.5 kW, suited for demanding welding applications with greater penetration and speed.
The AL-IN 600F is the highest-powered model, delivering 600W of fibre laser power with a peak pulse power of 6 kW and pulse energy of 60J. Designed for heavy-duty production welding, it handles large workpieces with precision.
Laser Type
The AL-IN series is available with both Nd:YAG solid-state lasers (1,064 nm) and fibre lasers (1,070 nm). The Nd:YAG models (120W to 300W) focus on pulsed welding, while the fibre laser models (150F to 600F) support both pulsed and CW modes. These lasers deliver pulse energy up to 90J and spot sizes ranging from 0.2 mm to 4 mm, making them suitable for precision welding of both delicate and large components.

Laser Systems
Laser Welding
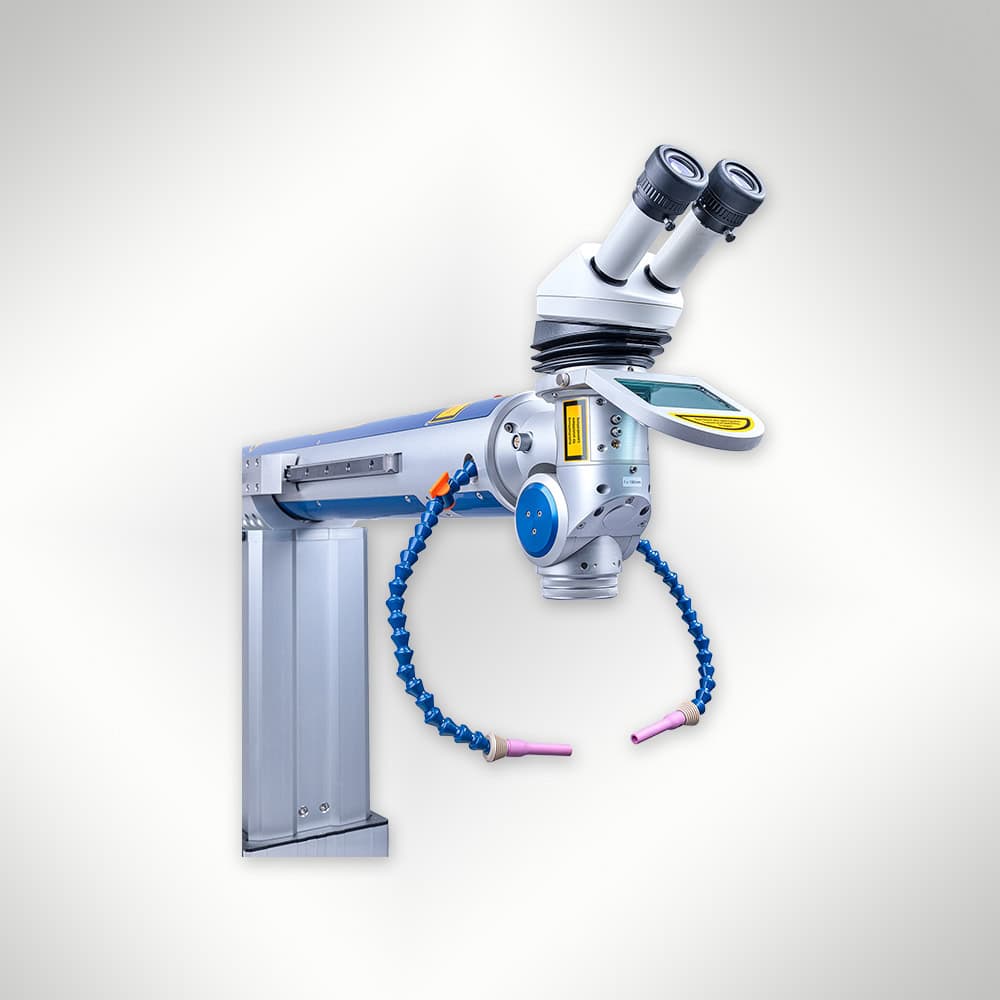
The AL-IN by Alpha Laser is a stationary laser welding system designed for precision welding across a variety of industrial applications, including tool repair, production, and fine-detail work. Available in both Nd:YAG (120W to 300W) and fibre laser configurations (150F to 600F), it offers pulsed and continuous wave (CW) welding modes for optimal control. The system features a movable laser resonator and a motorised X, Y, Z axis, allowing for flexible component positioning. The ergonomic touch display and AL-DRIVE joystick ensure user-friendly operation, while optional accessories like rotary axes, wire feeders, and powder deposition systems further enhance its capabilities. The AL-IN is ideal for manufacturing and maintenance tasks, ensuring high-precision results on both small and large components.
Send a Product Request
Product Form
Contact form for product pages
"*" indicates required fields
Laser Cleaning
Related Laser Cleaning Systems
Answering Your Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
Both laser marking and wafer sorting are integral to maintaining high-quality standards in semiconductor production. Laser marking provides permanent identification of each component, enabling traceability and facilitating the tracking of products throughout their lifecycle. Wafer sorting ensures that only functional dies advance to the packaging stage, effectively filtering out defective units early in the process. Together, these processes help minimise errors, reduce waste, and ensure that only components meeting strict quality criteria reach the market.
Wafer sorting, also known as wafer testing, is a process performed during semiconductor fabrication where each die (individual chip) on a silicon wafer is electrically tested for functionality. The primary purpose of wafer sorting is to identify non-functional or defective dies before they proceed to packaging, thereby preventing the assembly of faulty components. This step is crucial for enhancing overall yield, reducing manufacturing costs, and ensuring the reliability of semiconductor devices.
Laser marking is a process that uses focused laser beams to create precise, permanent marks on materials. In the semiconductor industry, this technique is essential for inscribing critical information onto wafers. The high precision of laser marking ensures that even microscopic marks are clear and readable, facilitating effective traceability and quality control throughout the manufacturing process.
The AL3D-METAL 200 is particularly suited for industries requiring high precision and intricate designs, such as precision mechanics, medical technology, dental, and jewellery sectors, as well as research and development laboratories. Its ability to produce complex geometries with fine detail makes it ideal for creating customised components, prototypes, and small series productions. The printer’s efficient material usage and safe powder handling are advantageous when working with high-value materials, making it a valuable tool for producing high-quality metal parts across various applications.
The AL3D-METAL 200 features a closed powder circuit that prevents operator contact with metal powders during the entire printing process, enhancing workplace safety. Its intelligent cartridge system simplifies material supply, enables quick process preparation, and ensures high material utilisation, which is particularly beneficial when working with expensive or precious metals. Additionally, the system includes the AL3D-CABIN unpacking station, providing a closed process chamber for the safe separation of sintered components from residual powder and facilitating the collection and potential reuse of leftover material.
The AL3D-METAL 200 is a 3D metal printer developed by ALPHA LASER GmbH, designed for the additive manufacturing of high-precision metal components. Key features include a 200 W fibre laser with a 50 µm focus diameter, a closed powder handling system for enhanced safety, an innovative cartridge system for efficient material usage, and a compact footprint of 600 × 617 mm, making it suitable for environments with limited space. The printer supports a variety of materials, including iron alloys, nickel-based alloys, cobalt-chrome alloys, precious metals, and reactive metals.
Laser hardening is primarily applied to ferrous metals, including various steels and cast irons, that have sufficient carbon content to undergo martensitic transformation. Industries such as automotive, aerospace and mechanical engineering utilise laser hardening to enhance the wear resistance and lifespan of components like gears, camshafts, and moulds. The process is particularly advantageous for large or complex parts, as mobile laser hardening systems can treat these components in situ, reducing downtime and eliminating the need for disassembly.
Laser hardening offers several benefits compared to conventional techniques:
- Precision and Control: The laser allows for exact control over the area being hardened, enabling selective treatment of specific surfaces without affecting the entire component.
- Minimal Distortion: Due to localised heating and rapid self-quenching, there is reduced thermal distortion, preserving the component’s dimensional accuracy.
- No Need for External Quenching: The process utilises the material’s own mass to cool the heated area, eliminating the requirement for external quenching media like water or oil.
- Efficiency: Laser hardening is a fast process, often completed in seconds, leading to significant time and energy savings.
Laser hardening is a surface treatment process that uses a high-powered laser beam to heat the surface layer of a metal component to its austenitizing temperature. This rapid, localised heating is followed by self-quenching, where the surrounding material cools the heated area quickly, transforming it into martensite—a hard and wear-resistant microstructure. This method enhances the surface hardness and durability of metal parts without the need for external quenching media.
Laser Cladding can be used for metals Such as stainless steel, nickel-based alloys, cobalt-based alloys, and titanium.
Reviews
Don't Just Take Our Word for It
Our Customers

Talk to Us!
Connect with our Technical & Support Team.